When you access a website via Internet Explorer, the browser first connects to your domain name system server, which can often be provided by your ISP. The DNS server converts a website’s human-readable name (for example, “example.com”) to a numerical IP address.
These DNS records are cached in a systemwide DNS cache for faster retrieval. In rare cases, incorrect DNS entries might be kept, causing difficulties connecting websites. Use the “ipconfig” command to clear the systemwide DNS cache that Internet Explorer uses.
How to Flush DNS
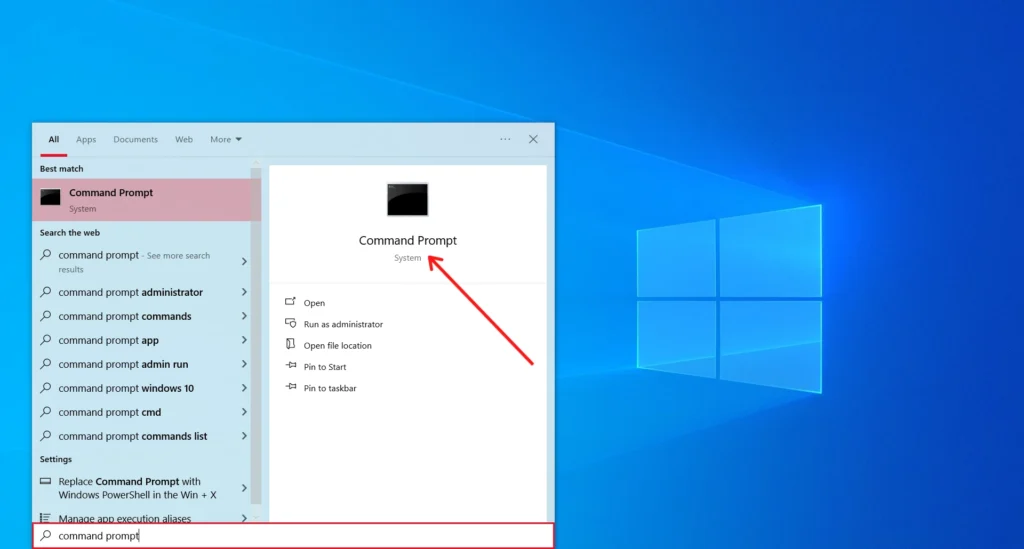
Click “Start,” then type “Command Prompt” into the search bar at the bottom of the menu and hit “Enter.”
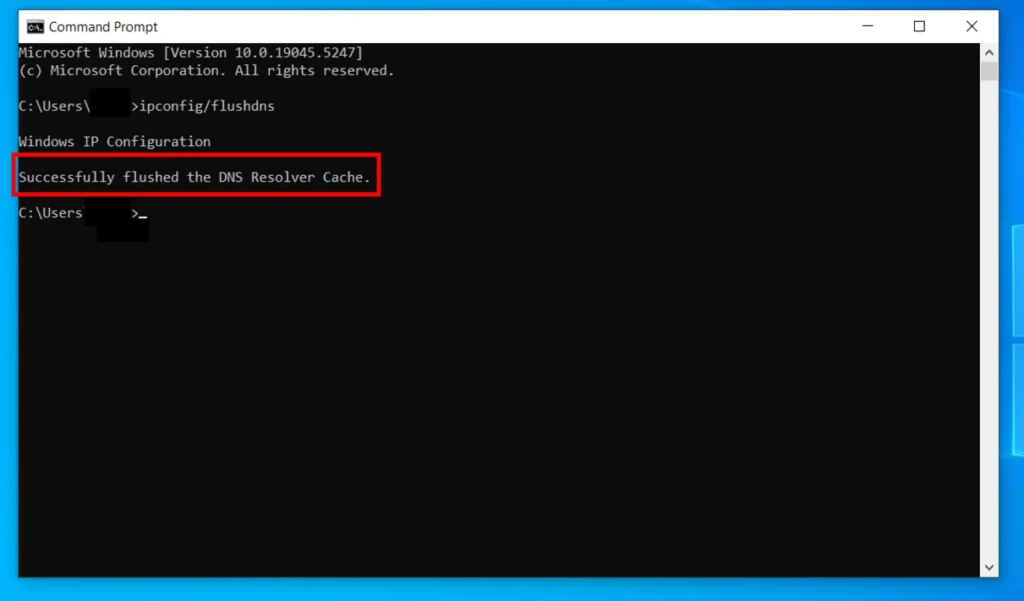
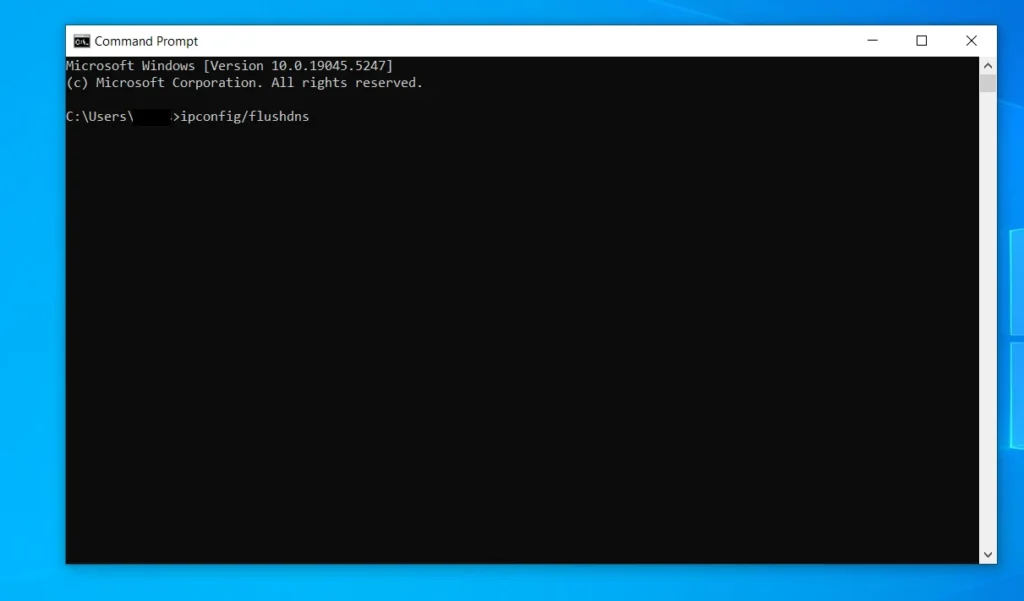
In the Command Prompt window, type “ipconfig /flushdns” (without the quotes).
To clear your DNS cache, use the “Enter” key. The keyword “Successfully Flushed the DNS Resolver Cache” will show on your screen.