In the field of modern medicine, diagnostic and interventional radiology plays a pivotal role in the accurate diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions. This branch of radiology combines advanced imaging technologies with minimally invasive procedures to provide precise and efficient healthcare solutions. In this article, we will delve into the world of diagnostic and interventional radiology, exploring its applications, techniques, and the benefits it offers to patients.
Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology: A Closer Look
The Importance of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology
Diagnostic and interventional SepStream radiology is a specialized field that utilizes various imaging techniques to diagnose diseases and guide minimally invasive procedures. It offers a non-invasive or minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods, reducing patient discomfort, recovery time, and hospital stays. By providing detailed images of internal structures, radiologists can accurately identify and evaluate abnormalities, enabling timely and precise interventions.
Evolution of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology
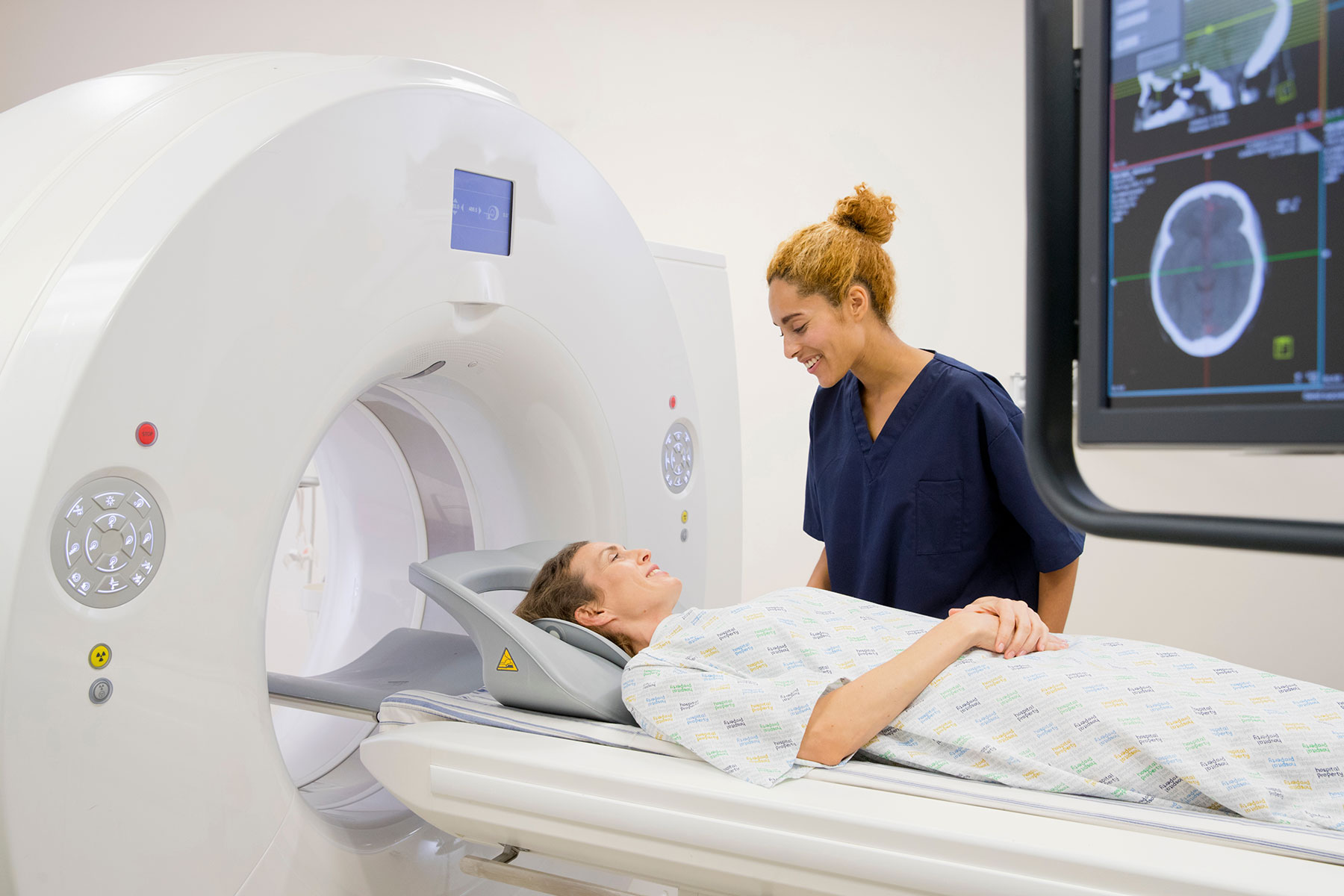
Over the years, diagnostic and interventional radiology has evolved significantly, owing to advancements in imaging technologies and interventional procedures. From the humble beginnings of X-ray imaging to the introduction of computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and fluoroscopy, this field has witnessed groundbreaking innovations that revolutionized medical imaging.
Today, interventional radiologists employ a wide range of techniques, such as angiography, biopsies, and catheter-based therapies, to deliver targeted treatments directly to affected areas.
Applications of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology
Diagnostic and interventional radiology finds applications across various medical specialties, from cardiology to oncology. Let’s explore some of the critical areas where this field plays a crucial role:
1. Cardiovascular Radiology
Cardiovascular radiology focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of heart and blood vessel diseases. Radiologists employ techniques like angiography, cardiac CT, and MRI to evaluate the structure and function of the cardiovascular system. These imaging modalities provide detailed information about blockages, aneurysms, and other abnormalities, enabling precise interventions such as angioplasty, stent placement, and embolization.
2. Neuroradiology
Neuroradiology deals with the imaging and treatment of diseases affecting the brain, spine, and nervous system. It involves techniques like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography angiography (CTA), and myelography. These imaging methods help diagnose conditions like strokes, brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, and multiple sclerosis. Interventional procedures like cerebral angiography and endovascular coiling are also performed for the treatment of aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations.
3. Musculoskeletal Radiology
Musculoskeletal radiology focuses on diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the bones, joints, and soft tissues. X-rays, CT scans, and MRI are commonly used imaging modalities in this specialty. Radiologists can accurately detect fractures, tumors, arthritis, and other musculoskeletal abnormalities. Interventional procedures like joint injections, arthrography, and bone biopsies aid in providing targeted treatments and pain management for various orthopedic conditions.
4. Abdominal and Pelvic Radiology
Abdominal and pelvic SepStream radiology involves the imaging and diagnosis of conditions affecting the abdomen and pelvis. Techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are used to assess organs like the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and reproductive organs. Radiologists can identify tumors, cysts, gallstones, and other abnormalities in these regions. Interventional procedures like percutaneous biopsy, drainage, and tumor ablation are also performed for therapeutic purposes.
5. Oncologic Imaging
Oncologic imaging plays a crucial role in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment planning of cancer patients. Various imaging techniques like PET-CT, MRI, and ultrasound are employed to assess tumors and metastases. Radiologists work closely with oncologists to identify the extent of the disease and plan appropriate treatment strategies, including image-guided biopsies and radiofrequency ablation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the role of a radiologist in diagnostic and interventional radiology?
Radiologists are medical doctors who specialize in interpreting medical images obtained through diagnostic and interventional procedures. They play a crucial role in diagnosing diseases, guiding treatment decisions, and performing minimally invasive procedures. Their expertise in interpreting complex images helps in providing accurate diagnoses and ensuring patient safety during interventions.
2. How safe are the procedures performed in diagnostic and interventional radiology?
Diagnostic and interventional radiology procedures are generally considered safe. Most interventions are minimally invasive and carry fewer risks compared to traditional surgeries. However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications. Radiologists undergo extensive training to minimize risks and ensure patient safety. They carefully evaluate each case, considering the potential benefits and risks before proceeding with any intervention.
3. What are the advantages of diagnostic and interventional radiology over traditional surgical methods?
Diagnostic and interventional radiology offers several advantages over traditional surgical methods, including:
- Minimally invasive procedures: Many interventions are performed through small incisions or using catheters, reducing trauma and promoting faster recovery.
- Reduced risk and complications: Minimally invasive procedures carry a lower risk of infection, bleeding, and other complications associated with open surgeries.
- Targeted treatments: Interventional radiologists can precisely deliver therapies directly to affected areas, minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
- Shorter hospital stays: Minimally invasive procedures often require shorter hospital stays compared to traditional surgeries, leading to cost savings and improved patient comfort.
4. How do radiologists stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in diagnostic and interventional radiology?
Radiologists are committed to lifelong learning and professional development. They attend conferences, workshops, and scientific meetings to stay updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and interventional radiology. They also participate in research and collaborate with other medical professionals to enhance their knowledge and expertise.
5. Are there any risks associated with radiation exposure during diagnostic imaging?
Diagnostic imaging techniques that use radiation, such as X-rays and CT scans, involve minimal radiation exposure. The benefits of accurate diagnosis generally outweigh the potential risks of radiation. However, radiologists and technologists follow strict protocols to minimize radiation exposure and ensure patient safety. Pregnant women and children are given special considerations to further reduce radiation exposure.
6. How can patients prepare for a diagnostic or interventional radiology procedure?
Patients are usually provided specific instructions by their healthcare provider before a diagnostic or interventional radiology procedure. These instructions may include fasting requirements, medication adjustments, or the need for a contrast agent. Patients need to follow these instructions carefully and inform their healthcare team about any allergies, medical conditions, or medications they are taking.
Conclusion
Diagnostic and interventional radiology has revolutionized the way we diagnose and treat various medical conditions. Through advanced imaging techniques and minimally invasive interventions, radiologists provide accurate diagnoses, targeted therapies, and improved patient outcomes. From cardiovascular and musculoskeletal disorders to neurological conditions and oncology, this specialized field continues to contribute significantly to modern healthcare. As technology continues to advance, diagnostic and interventional radiology will undoubtedly play an even more crucial role in shaping the future of medicine.